What is Saffron
What is saffron?
Saffron is a small plant with a height of 10 to 30 cm with the scientific name Crocus S ativus . It belongs to the Iridaceae family which is a family of asparagus-like plants with underground stems and linear or stripy leaves that have a six-parted inflorescence, a three-parted cream, and three stamens.
From the middle of a bulb, which is covered with brown layers, a green stem with a number of narrow and long leaves emerges and from the center of the leaves, a flowering stem appears leading to one to three flowers. Saffron is propagated through its bulb, and the bigger the bulb, the higher the quality of the saffron can be produced. Saffron is an autumn plant whose flowers open in the cold and at sunrise, and farmers have little time to harvest it. The flowers have 6 purple petals, which may be flowery or purple in some species.
Each flower has 3 flagella and a pistil leading to a red-to-orange trilobed stigma. The useful part of the saffron plant is the three-branched flag or stigma, which is known as saffron. This plant is abundantly planted in eastern Iran.
History and the origin
Some historical sources mention that saffron history can go back to 5,000 years ago in Iran. As proof, a botanical book belonging to the Assyrian era is written about the saffron flower.
200 years ago, a land from Samarkand and Bukhara in Afghanistan to Kashmir in India and Damghan in Iran had been called Great Khorasan. Currently, Khorasan is a large part of eastern Iran, where saffron is being planted in different areas of this land. It is noted that the world’s highest quality saffron is produced in Khorasan, Iran, and is transported by merchants to numerous parts of the world.
Producer countries
Different countries in the world produce saffron. In Europe, Spain, Italy, and Greece; in Africa, Egypt, in Asia, Iran, Afghanistan, and India are the major producers of spice. Every year, various statistics on saffron production in the world are published by international organizations and institutions. Sometimes they disagree with each other, but in all published lists, Iran has been introduced as the first and largest producer. Most of the world’s saffron is produced in Iran specifically in Khorasan. Unfortunately, it is observed that some countries export the saffron that was imported this valuable substance from Iran and they export again to other countries under their names.
In Ariaramnes, we are proud to import saffron pistils directly from the highest standard field from Khorasan, Iran.
Analysis and the quality
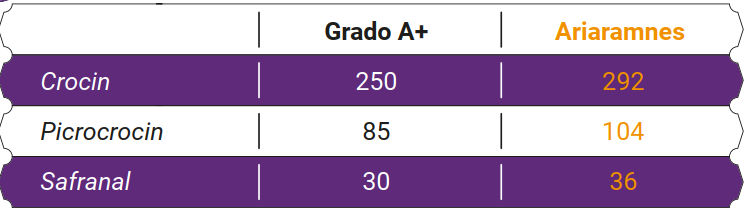
Scientifically, the qualities of saffron are measured and categorized by testing and measuring three factors that are crocin, safranal, and picrocrocin. Moreover, there are some other tests to verify the level of contamination and the healthiness of the saffron after processing and drying. These tests are based on the available standards that have been defined by the International Organization for Standardization, known as ISO.
ISO 3632 has been identified as the main standard for determining the quality of saffron in the world and the national standard of Iran is also in accordance with the ISO 3632 standard.
The main tested compounds of saffron are crocin, picrocrocin, and safranal.
Crocin
It is one of the most important substances of saffron which is responsible for the color of the saffron . Crocin is a diester and disaccharide composed of gentiubius and crostin carboxylic acid and is one of the few carotenoids that is soluble in water.
Safranal
Safranal is the main aromatic substance in saffron, and it makes up about 60% of the volatile compounds of this spice . The smell of saffron is the result of the aroma (a feeling between smelling and tasting) of some volatile oils and a special essential oil that is present in this substance, which is found in fresh saffron in the form of picrocrocin. It is non-volatile, but it decomposes due to heat and over time, and the volatile safranal aldehyde is released.
Picrocrocin
The bitter taste of saffron as a plant material is related to the picrocrocin. picrocrocin forms the dominant taste of saffron.
Saffron tests are in accordance with the ISO 3632 standard to check the amount of crocin, picrocrocin safranal, and other substances in it.
Regarding the investigation of the hygienic process of harvesting and collecting saffron, microbial tests are also carried out to check the level of contamination of harvested saffron.
In today’s agriculture, the use of fertilizers and chemicals to increase the yield of the soil has been increased. Therefore, tests are also carried out on saffron to check the residue of agricultural toxins.
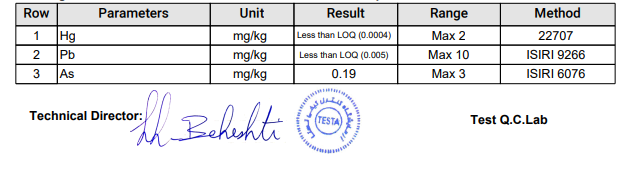
Human interventions in water and land resources are responsible for the entrance of heavy metals into the food cycle. In order to check the amount of these substances, analyzes are being conducted to check the amount of heavy metals in harvested saffron (results of heavy metal tests).
In the saffron standard, the maximum metal pollutants should be a maximum 3 mg/kg for arsenic, 10 mg/kg for lead, 2 mg/kg for mercury (according to the European standard).
The quality of saffron depends to a large extent on its processing after harvesting and the storage conditions of the product. The effect of temperature, storage time, and humidity have severe effects on the chemical characteristics of saffron stigma, including color, aroma, and bitterness. With increasing temperature, the intensity of color decreased significantly and it has a direct effect on reducing the aroma as well .
They address categories
Saffron can be classified in different ways The most common of which is the classification based on the cut of the stigma. The color spectrum of the stigma consists of white, yellow, orange, and red. The yellow end is called the cream, and in common terms, the saffron cream is called the tail, and the white part of the stamen is called the root.
Sargol, Negin, Semi -Negin, and Pushal are different parts of saffron stigma which have different names according to the cut area.
Due to the thickness and length of the saffron pistil , these names are placed next to other terms that in a way indicate the quality of the product, such as:
Super Negin : An elongated Negin with large pistils .
Common Negin : A Negin that is commonly available in the market.
First harvested Negin : which is related to the first arrangement at the beginning of the season, has a good fragrance and color.
Ariarmanes is an expert just to provide Super Negin saffron on your table.
The method of drying saffron also creates a kind of classification for it, usually drying is done traditionally and by machine. In the case that drying is done by a machine since in the process pressure is also used, this type is called pressure ironing saffron . Sometimes it is also called pressed saffron .
According to the international standard of saffron 3632 and the national standard organization of Iran, saffron is divided into 5 major categories, and these 5 categories should have the following properties and characteristics:
Premium cut pistil saffron: In terms of appearance should have a maximum of 0.5% cream along with stigma and color number (crocin) at least 220
First grade string: should have a maximum of 5% cream along with the stigma and the color number (crocin) should be at least 200.
2nd grade string: a maximum of 10% cream along with the stigma and the color number (crocin) is at least 180.
3rd grade string: should have a maximum of 20% cream along with the stigma and the color number (crocin) should be at least 150.
4th grade string: has a maximum of 30% cream along with the stigma and the color number (crocin) is at least 130
Other items are also effective in determining the quality of saffron which is determined in the results of the tests.
Features of packaging
Storing saffron is an important issue that should be paid attention to. We talked about the effect of heat on saffron in the above sections, so after harvesting and the cleaning process, saffron is transferred to a warehouse with a temperature of 12 to 17 degrees Celsius. In these warehouses, the humidity is within 5% is controlled. By keeping in mind that light has a great effect on the color of saffron, saffron is stored in dark or very dim warehouses.
Accordingly, for the packaging of saffron, it should be considered that the packaging should be in a way that prevents the penetration of moisture into the saffron and has the least heat exchange with the environment, Most importantly, the saffron should be covered in a way that the least of the light will reach it.
Packs of Ariaramnes
The usages
Food
The ingredient that plays a big role in the taste of the food is spice, and basically, it is not possible to cook a tasty food without using all kinds of it. Even if the best quality ingredients are used in cooking, the spice is what makes the taste of the food. A group of spices help the food to be fragrant and remove the smell of raw materials. Another group helps the cook to give the food a new color and look like a painter, and another group helps to change the taste of the food.
The extraordinary feature of saffron is its unique aroma and coloring. it is often used in cooking to flavor and color food.
The color combination of saffron is an exciting and passionate combination, and these colors, along with their aroma, stimulate the brain and increase appetite.
Antioxidant compounds in it have beneficial effects that are not comparable to conventional chemicals, and therefore it can be used as a natural substitute for artificial preservatives in food.
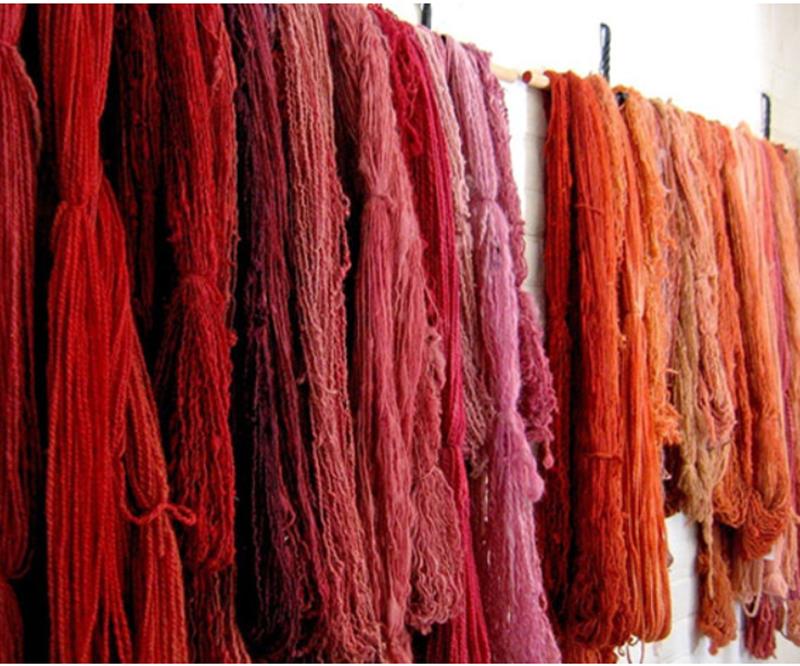
dye exquisite fabrics
From the far past until now, it has been used to color fabric fibers, especially expensive fabrics such as silk. The reason for this is not only the beautiful color of saffron but also its disinfecting properties. I t is certain that in addition to achieving an amazing colored fabric, any possibility of mold, fungus, and spoilage of the fabric is eliminated.
Therefore, in ancient times , these fabrics were used in the courts of kings.
In addition to the use of this precious plant in textiles, we can mention the dyeing of carpet wefts. In Iran, special tarpods such as silk are used for the weaving of special carpets and sometimes saffron color is used to color it.
Due to the high cost of saffron, this dye cannot be used for a large volume.
writing important works
In the protection and restoration of old works, the question of what the main components of these works are always mentioned . Spectroscopy is one of the conventional ways to identify the constituent components of the artworks . These spectrographs show that in written works, saffron has been used to decorate manuscripts. Various methods and methods of using saffron color in book design and Diagnosing the time period require research and examination of the process. The study of ancient calligraphy treatises, and texts related to the art of book design, as well as the guidance of contemporary masters shows that saffron was used in the decoration of religious booksin a wide time span from the third to the twelfth century. Colored pages of the Shahnameh (an important ancient Persian poem book) , colored miniatures with red color.
cosmetic industries
Today, saffron is widely used in the cosmetics industry. In recent years, this space has been of great interest for use in cosmetics and perfumery. Its main components and their characteristics determine the uses of saffron in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
The main use in the cosmetic and health industries is related to a substance called “crocin”, which is one of the main components of saffron. This material is a natural red pigment found in the saffron flower. Crocin, as a natural pigment, is used for coloring in the production of cosmetic and hygiene products such as lotion, cream, lipstick, shampoo, etc.